Tornado Warning in Iowa: Causes and Formation
Tornadoes are violent rotating columns of air that extend from the base of a thunderstorm cloud to the ground. They are one of the most destructive forces of nature and can cause widespread damage and loss of life. Iowa is one of the most tornado-prone states in the United States, and it is important to understand the causes and formation of tornadoes in order to stay safe.
Tornadoes are formed when warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico meets cold, dry air from the north. This creates an unstable atmosphere that can lead to the development of thunderstorms. If the conditions are right, these thunderstorms can produce tornadoes.
The process of tornado development begins with the formation of an updraft. An updraft is a rising column of warm air that forms inside a thunderstorm cloud. As the updraft rises, it cools and condenses, releasing latent heat. This heat helps to fuel the updraft, causing it to rise even higher.
As the updraft rises, it begins to rotate. This rotation is caused by the Coriolis effect, which is a force that deflects moving objects to the right in the Northern Hemisphere. The rotation of the updraft creates a vortex, which is a funnel-shaped cloud that extends from the base of the thunderstorm cloud to the ground.
If the vortex becomes strong enough, it can reach the ground and become a tornado. Tornadoes can vary in size, but they are typically about 1,000 feet wide and can reach speeds of up to 300 miles per hour.
The intensity and duration of a tornado is determined by a number of factors, including the strength of the updraft, the amount of moisture in the air, and the wind shear. Wind shear is the difference in wind speed and direction between two levels of the atmosphere. Strong wind shear can help to intensify a tornado and make it last longer.
Tornadoes can cause widespread damage and loss of life. They can destroy homes and businesses, uproot trees, and even kill people. It is important to be aware of the risks of tornadoes and to take precautions to stay safe.
Tornado Warning Systems and Preparedness
Tornado warning iowa – Iowa has implemented a comprehensive network of tornado warning systems to safeguard its citizens. The National Weather Service (NWS) issues watches and warnings to alert communities of potential and imminent tornado threats.
Early detection and timely warnings are crucial for effective tornado preparedness. The NWS utilizes advanced radar and weather monitoring technologies to detect tornado formation and issue warnings promptly.
Evacuation Routes and Shelter Locations
Developing a tornado preparedness plan is essential for every household. This plan should include designated evacuation routes and identified shelter locations.
- Evacuation Routes: Plan multiple evacuation routes in different directions to avoid potential road closures or obstructions.
- Shelter Locations: Identify sturdy buildings or underground structures that can provide adequate protection during a tornado. Consider schools, community centers, or basements.
Historical Tornado Impacts in Iowa: Tornado Warning Iowa
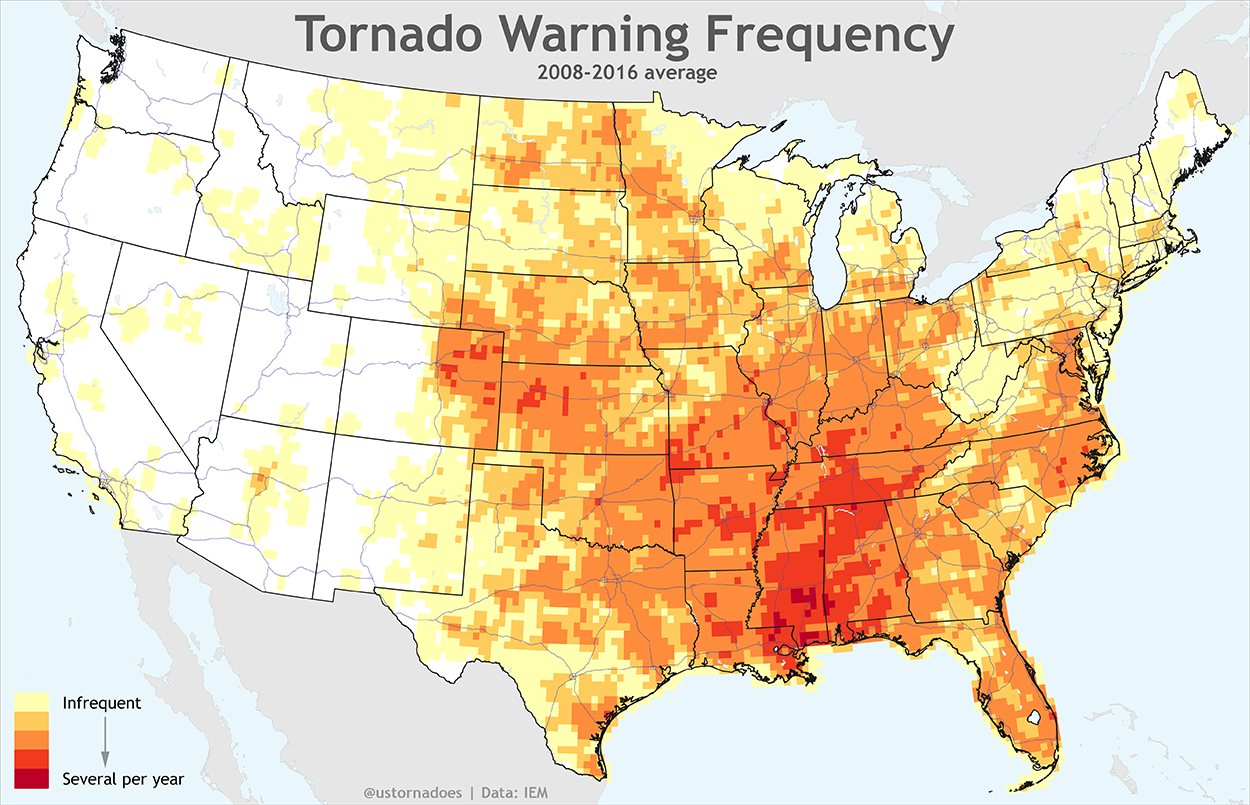
Iowa has a long and well-documented history of tornadoes. The state is located in the heart of Tornado Alley, a region of the central United States that experiences a high frequency of tornadoes each year. Iowa’s tornadoes have caused significant damage and loss of life throughout the state’s history.
The first recorded tornado in Iowa occurred in 1844. Since then, there have been over 1,500 tornadoes reported in the state. The most active tornado year in Iowa was 1966, when there were 103 tornadoes reported. The deadliest tornado in Iowa history occurred in 1953, when an F5 tornado killed 11 people and injured over 100.
Notable Tornado Events
Some of the most notable tornado events in Iowa history include:
- The Sioux City Tornado (1953): An F5 tornado struck Sioux City on June 25, 1953. The tornado killed 11 people and injured over 100. The tornado caused extensive damage to the city, destroying over 500 homes and businesses.
- The Parkersburg Tornado (2008): An F5 tornado struck Parkersburg on May 25, 2008. The tornado killed six people and injured over 100. The tornado caused extensive damage to the town, destroying over 100 homes and businesses.
- The Des Moines Tornado (2018): An EF3 tornado struck Des Moines on March 5, 2018. The tornado killed two people and injured over 20. The tornado caused extensive damage to the city, destroying over 100 homes and businesses.
Trends and Patterns
The frequency and severity of tornadoes in Iowa has varied over time. However, there are some general trends and patterns that can be observed.
- Tornadoes are most common in the spring and summer months. The peak tornado season in Iowa is from April to June.
- Tornadoes are more likely to occur in the afternoon and evening hours. The most common time for tornadoes to occur is between 4 and 8 pm.
- Tornadoes are more likely to occur in rural areas. However, tornadoes can also occur in urban areas.
Tornado Safety and Mitigation Strategies
Tornadoes are destructive forces of nature that can cause widespread damage and loss of life. However, by understanding the risks and taking appropriate safety measures, individuals can significantly reduce their vulnerability to these storms.
Before a Tornado Warning
- Develop an emergency plan that includes a designated safe place to seek shelter, evacuation routes, and communication methods.
- Identify sturdy buildings or underground structures in your area where you can take refuge during a tornado.
- Secure loose outdoor objects such as lawn furniture, trampolines, and grills.
- Stay informed about weather forecasts and be prepared to act quickly if a tornado warning is issued.
During a Tornado Warning, Tornado warning iowa
- Seek shelter immediately in a sturdy building or underground structure.
- Go to the lowest level of the building and stay away from windows and exterior walls.
- Cover yourself with blankets or pillows for protection from flying debris.
- Stay calm and follow the instructions of emergency responders.
After a Tornado Warning
- Check for injuries and seek medical attention if necessary.
- Assess the damage to your property and contact your insurance company.
- Stay informed about official updates and follow the instructions of emergency responders.
- Be cautious of downed power lines and other hazards.
Importance of Seeking Shelter in Sturdy Buildings or Underground Structures
During a tornado, the most important thing you can do is seek shelter in a sturdy building or underground structure. This provides the best protection from the high winds and flying debris that can cause serious injury or death.
Role of Tornado-Resistant Construction Techniques in Mitigating Damage
Tornado-resistant construction techniques can significantly reduce the risk of damage to buildings during a tornado. These techniques include reinforcing walls and roofs, using impact-resistant windows, and installing tornado shelters. By incorporating these techniques into building design, communities can make their structures more resilient to these powerful storms.
Tornado Research and Forecasting

In the relentless pursuit of protecting lives and property, scientific research plays a pivotal role in advancing our understanding of tornadoes and enhancing our ability to forecast them. Ongoing research efforts are dedicated to improving tornado prediction and detection through the advancement of weather radar technology, satellite imagery analysis, and computer modeling.
Weather radar, a cornerstone of tornado detection, utilizes Doppler technology to measure the velocity and direction of wind within a storm. By analyzing these data, meteorologists can identify areas of rotation and pinpoint the potential for tornado formation. Satellite imagery provides valuable insights into the development and movement of storm systems, allowing forecasters to track their progress and anticipate areas at risk.
Computer Models
Computer models, sophisticated mathematical simulations, play a crucial role in tornado forecasting. These models ingest vast amounts of data from weather stations, radar systems, and satellites, enabling meteorologists to create detailed simulations of atmospheric conditions. By running these simulations, forecasters can predict the likelihood, timing, and potential path of tornadoes, providing critical lead time for warnings and emergency response.
Despite these advancements, challenges and limitations remain in tornado forecasting. The unpredictable nature of tornadoes and the often short lead time between formation and touchdown present significant hurdles. However, ongoing research and collaboration among scientists and meteorologists are continuously pushing the boundaries of our understanding and improving our ability to protect communities from these devastating storms.